Essential Safety Tips for Cryogenic Nitrogen Plants
Introduction
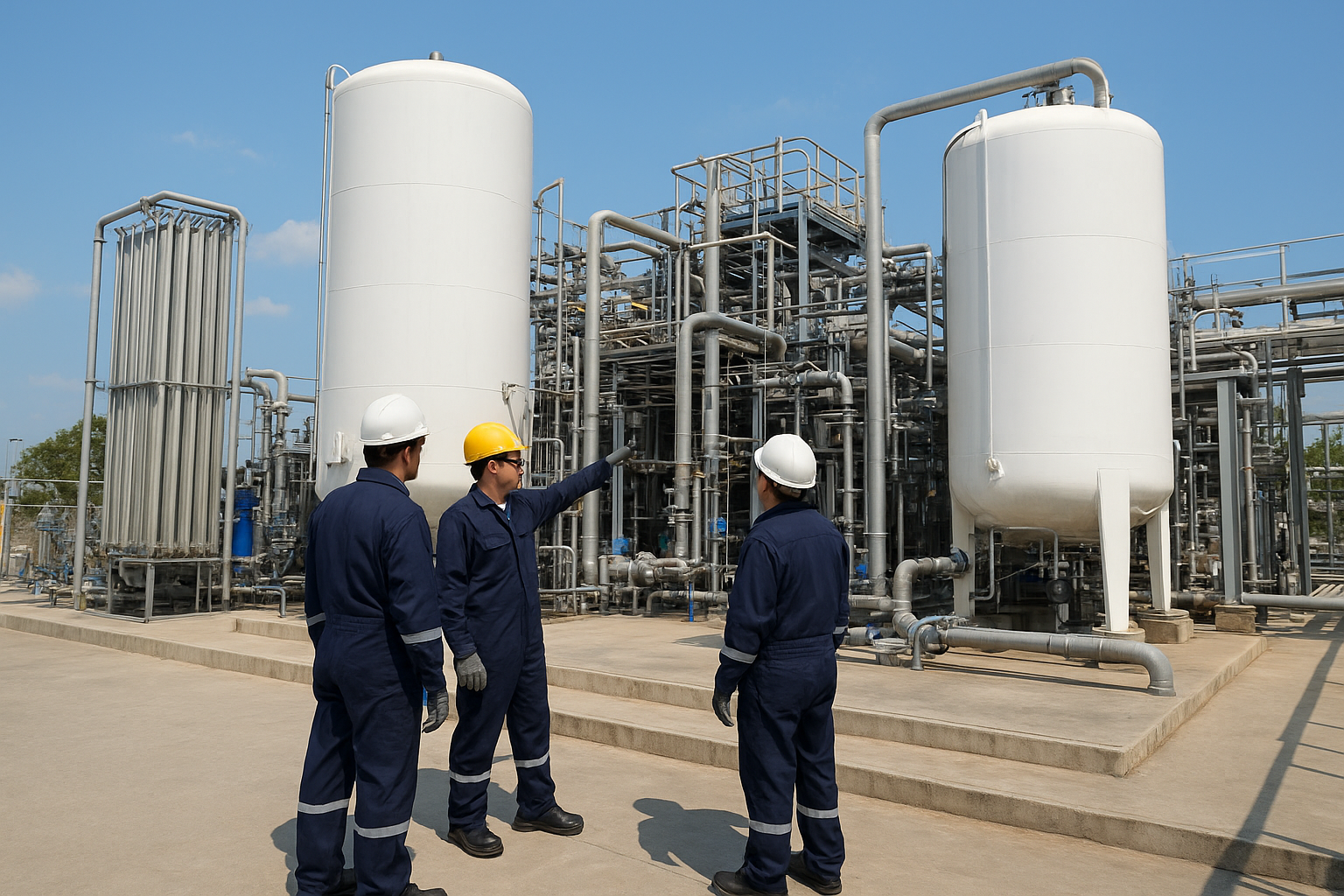

Cryogenic nitrogen plant safety is not optional — it is a core engineering discipline. Every activity inside a cryogenic nitrogen plant, from compressor start-up to cold box operation, carries inherent risk due to extremely low temperatures, high pressures, and oxygen displacement hazards.
Without structured procedures, trained operators, and proper safeguards, small oversights can quickly escalate into serious incidents.
This guide explains essential safety practices for cryogenic nitrogen plants, helping engineers prevent start-up issues, equipment damage, and operational hazards before they occur.

1. Understanding Cryogenic Hazards
Cryogenic nitrogen plant hazards differ significantly from normal industrial environments. Ultra-low temperatures, rapid pressure changes, and oxygen displacement create risks that require strict engineering controls and disciplined operation.
For deeper technical safety principles, refer to the Air Products and Chemicals technical safety resources, which explain cryogenic handling best practices used across the industrial gas industry.
Most common hazards in cryogenic nitrogen plants include:
Extreme Cold: Direct contact can cause instant frostbite or damage to eyes and lungs.
Material Embrittlement: Metals, seals, and gaskets can fracture at cryogenic temperatures.
Oxygen Enrichment: Leaks in nitrogen lines can lead to air condensation, increasing fire risk.
Pressure Build-Up: Boil-off from liquid nitrogen rapidly increases pressure in confined vessels.
Asphyxiation: Nitrogen displaces oxygen, creating invisible suffocation hazards.

2. Equipment & Area Safety
The physical design of a cryogenic nitrogen plant facility forms the first line of protection. Proper insulation, pressure protection, and safe access control reduce the likelihood of freezing damage, overpressure events, and accidental exposure.
Key Equipment Safety Measures:
Insulated Pipelines & Valves: Prevent frost formation and protect against surface burns.
Pressure Relief Valves: Regularly calibrated to avoid overpressure conditions.
Safety Barriers & Signage: Restrict unauthorized entry into cryogenic zones.
Drip Trays & Spill Basins: Capture condensate and minimize ice accumulation.
Remote Shutoff Systems: Enable system isolation from a safe distance during emergencies.
Routine inspections, mechanical integrity checks, and strict maintenance schedules are non-negotiable. Safety valves are silent guardians — they must always be tested and documented to maintain cryogenic nitrogen plant safety standards.

“Operators should follow applicable OSHA workplace safety standards and recognized cryogenic safety guidelines to ensure compliance and safe operation.”

3. Safe Operating Practices in Cryogenic Nitrogen Plants
Even the safest design depends on disciplined operation. Cryogenic nitrogen plant safety performance is strongly influenced by operator behavior, adherence to SOPs, and consistent monitoring.
Best Practices:
Always wear approved PPE: cryogenic gloves, face shields, safety shoes, and insulated aprons.
Never bypass interlocks or alarms during operation or testing.
Follow standard operating procedures (SOPs) strictly — especially during startup and shutdown.
Maintain logbooks and digital records of every process deviation or alarm event.
Conduct safety drills and toolbox talks before critical operations.
👉 Engineers facing repeated instability during start-up should review Top 10 Common Problems During Nitrogen Plant Start-Up to understand typical failure patterns.
Safe operation is not about avoiding mistakes — it’s about building systems that anticipate and prevent them.
4. Instrumentation & Control Safety
Automation improves reliability, but poorly maintained instrumentation can introduce hidden risks. Reliable instrumentation and control systems in cryogenic nitrogen plants ensure safe shutdowns, alarm response, and stable operation.
Instrumentation Safety Checklist:
Verify all pressure and temperature transmitters are calibrated.
Test interlocks and emergency shutdown (ESD) systems regularly.
Validate DCS logic for high/low setpoints and trip conditions.
Maintain redundant instrumentation for critical parameters (e.g., product purity, storage pressure).
Ensure operators are trained in alarm response procedures.

At Graphic Medium Industrial, we emphasize “control awareness” — knowing not just what the system does, but why it reacts that way.
5. Personnel Training & Certification
A cryogenic nitrogen plant is only as safe as the people operating it. Structured training, certification, and repeated drills ensure operators recognize hazards early and respond correctly during abnormal situations.
Key Training Areas:
Cryogenic process fundamentals
PPE usage and emergency response
Control system familiarization (DCS/PLC)
Permit-to-work systems and lockout/tagout
First aid and fire safety
Many engineering teams are now adopting digital training modules and mini-courses focused on cryogenic safety and commissioning practices — available on demand, anytime.


6. Emergency Preparedness & Response for Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Safety
Despite strong preventive measures, emergencies can still occur. A clear emergency preparedness plan for cryogenic nitrogen plants reduces injury, downtime, and equipment damage by enabling rapid, coordinated response.
Essential Elements of Emergency Plans:
Clearly marked evacuation routes and muster points.
Oxygen monitoring systems in enclosed spaces.
Cryogenic first-aid kits and safety showers.
Fire extinguishers rated for cold-related hazards.
Periodic mock drills involving both plant and emergency teams.
Plants that conduct periodic mock drills and maintain oxygen monitoring systems experience significantly lower incident rates.

7. Digital Tools & Resources
Digital tools now play a major role in improving cryogenic nitrogen plant safety. Real-time monitoring, mobile inspections, and structured logs reduce human error and provide early warning of unsafe conditions.
Recommended Tools:
Digital checklists for commissioning and maintenance
QR-based equipment logs for faster traceability
Mobile dashboards for real-time plant status
Online training modules to refresh safety standards
At Graphic Medium Industrial, we integrate proven engineering logic into digital checklists, troubleshooting templates, and commissioning tools to simplify plant safety management.


8. Final Thoughts: Safety Is a Culture

Cryogenic nitrogen plant safety is not a checklist — it is a culture. From design and commissioning to daily operation and maintenance, every decision impacts reliability and personnel protection.
Teams that implement structured procedures, digital tools, and documented checks consistently achieve:
• Fewer shutdowns
• Safer operations
• Higher reliability
• Faster troubleshooting
“Ready to Improve Your Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Safety?”
Get instant access to practical safety checklists, commissioning logs, troubleshooting sheets, and proven engineering templates used by field engineers.
