Step-by-Step Guide to Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning (Startup to Performance Test)
In the world of industrial gases, precision defines success. Learn how to ensure safety, reliability, and performance during every stage of commissioning — from air compression to product output.

Introduction
Cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning is the stage where a facility truly comes alive — every valve, instrument, and control loop is methodically tested to confirm that the system performs exactly as designed. It is far more than starting equipment; commissioning is a structured validation process that proves safety, reliability, and performance under real-world operating conditions.
From verifying individual subsystems to achieving product purity at rated design capacity, cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning ensures the facility is ready for stable, long-term operation. When executed correctly, it prevents premature failures, minimizes unplanned downtime, and gives operators confidence in consistent, safe performance from day one.
While commissioning principles are often discussed in theory, real-world execution demands disciplined sequencing, documented readiness, and repeatable checks under site conditions. To support engineers during actual commissioning work, we have translated these field lessons into a practical [Cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning checklist] — a structured, step-by-step reference covering pre-start checks, start-up activities, and stabilization stages.
In more complex projects, commissioning challenges rarely exist in isolation. Issues often arise at the interfaces between process design, instrumentation, controls, and site execution. In such cases, experienced engineering judgment becomes critical — which is where our [industrial commissioning consulting] focuses: selective, scope-defined support aligned to real plant constraints rather than generic advisory models.
At Graphic Medium Industrial, we transform industry experience and established engineering principles into structured digital resources and practical tools — simplifying complex cryogenic procedures into accessible learning materials for engineers, trainees, and students.
This guide walks you through the complete cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning process — from preparation and system checks to final performance validation — with a strong emphasis on safety, instrumentation integrity, and operational stability at every stage.
This commissioning framework is based on repeated field commissioning cycles across cryogenic nitrogen plants, converted into structured digital checklists and diagnostic tools to support consistent, confident execution in real operating environments.
1. What Is Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning?
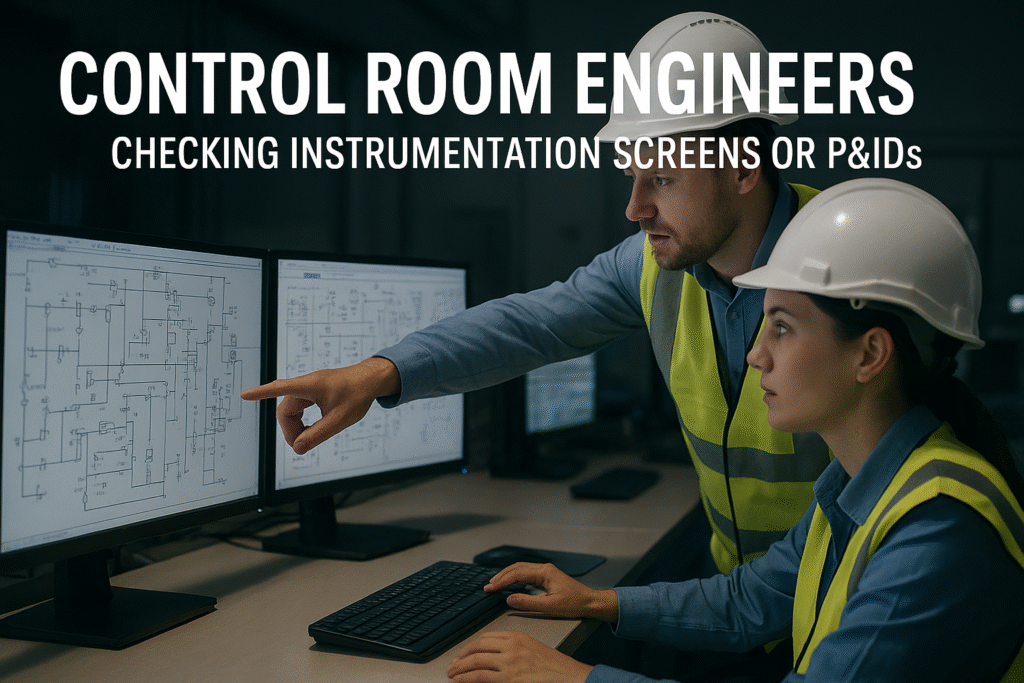
Cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning is a structured and systematic process of testing, calibrating, and verifying that all plant systems perform according to design parameters. It bridges the gap between installation and full-scale production — ensuring that mechanical, electrical, and process systems are safe, compliant, and ready for continuous operation.
Objectives:
Confirm all systems are installed, tested, and ready for operation.
Ensure safety interlocks, instruments, and utilities function as intended.
Bring the plant to design conditions — pressure, flow, and purity.
Handover the system to operations in stable, safe condition.
2. Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant – Process Overview
Before starting commissioning, engineers must clearly understand the process flow and critical equipment involved.
A typical cryogenic nitrogen plant works on separation of air components at very low temperatures (around –180°C to –196°C).
The process broadly involves five major steps:
Step 1: Compression of Atmospheric Air
The commissioning process begins with air compression, where atmospheric air is compressed using multi-stage air compressors. During cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning, this step involves verifying parameters such as discharge pressure, inter-stage temperature, vibration levels, and lubrication system health.
Key checks include:
Verifying all suction filters and valves are clean and correctly installed.
Monitoring compressor performance under various load conditions.
Ensuring all pressure safety valves are calibrated and functional.
A stable and efficient air compression system lays the foundation for smooth operation of downstream cryogenic processes.
For general engineering reference, you may consult publicly available compressor handbooks and resources from major compressor manufacturers.

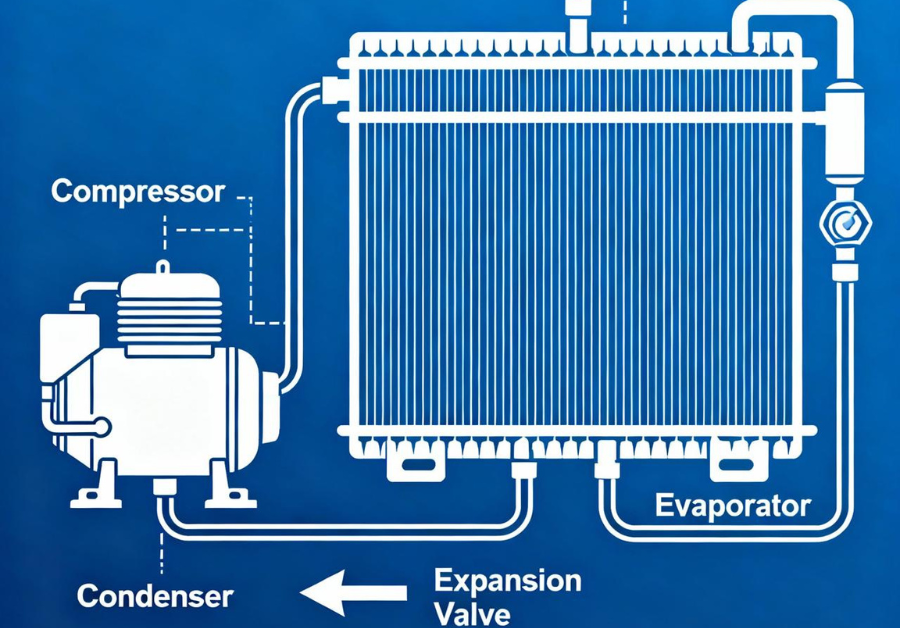
Step 2: Cooling of Air in Refrigeration System
Next comes air cooling, where the compressed air passes through a refrigeration unit to lower its temperature before purification. This is a vital stage in cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning, as it directly impacts energy efficiency and plant stability.
Commissioning engineers must:
Verify the performance of chiller units and expansion valves.
Inspect refrigerant charge levels and detect potential leaks.
Record temperature differentials across heat exchangers.
A well-commissioned refrigeration system ensures that the air entering the cold box remains within design limits, maintaining process integrity.
Step 3: Removal of Moisture, CO₂, and Impurities
In this phase, moisture and carbon dioxide (CO₂) are removed from the cooled air using molecular sieve–based purification units. These impurities can freeze under cryogenic conditions, so their removal is essential for safety and reliability.
Why Pretreatment Failure Causes Cold Box Freezing.
During cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning, the checklist typically includes:
Checking regeneration heater operation and cycle timing.
Verifying the efficiency of desiccant beds.
Monitoring dew point and CO₂ analyzer readings.
Consistent dew point readings confirm that the air is fully conditioned for entry into the cryogenic air separation unit (ASU).
For engineers assessing drying effectiveness and breakthrough risks during commissioning, the CO₂ & moisture impact guide explains how trace contaminants affect cold box performance, purity stability, and long-term operational reliability.
For deeper diagnostics, also see:
Step 4: Entry of Air into Cold Box for Separation Process
The cold box is the heart of the cryogenic nitrogen plant and plays a critical role during commissioning and performance stabilization.
During cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning, engineers focus on:
Verifying proper operation of control valves, expansion turbines, and heat exchangers.
Ensuring the column pressures and temperatures match design data.
Recording nitrogen purity and oxygen concentration in product gas.
This step determines whether the plant can achieve design capacity and product purity targets. Any variation at this stage must be carefully analyzed before moving to performance trials.
During initial cooldown and stabilization, the cold box temperature mapping sheet helps engineers track temperature gradients, identify maldistribution, and detect early signs of thermal imbalance before purity is affected.
If temperature imbalance or purity instability persists, engineers often need structured troubleshooting beyond startup checks.
For additional background on cryogenic science and safety principles, you may refer to publicly available resources from major industrial gas companies and technical organizations.

Step 5: Product Output and Delivery
Once the separation process is stabilized, the focus shifts to product delivery — ensuring that nitrogen purity, pressure, and flow meet specifications. During the final phase of cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning, engineers perform the performance guarantee test (PGT) or trial run.
This phase includes:
Testing product pipelines and valves for leaks.
Verifying control room instrumentation and alarms.
Recording nitrogen flow, purity, and power consumption data.
A successful trial run marks the completion of the commissioning phase, transitioning the system into steady-state operation.
Why Plants Fail Performance Guarantee Tests
unstable operation
refrigeration inefficiency
pretreatment breakthrough
control tuning
Read more: 

3. Pre-Commissioning Activities Prior to Start Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning

Before starting the actual process, pre-commissioning ensures readiness of all systems — mechanical, electrical, and instrumentation.
a. Documentation Review
Verify that all P&IDs, PFDs, and as-built drawings are up to date. Marking incorrect line numbers or missing tags at this stage prevents major errors later.
b. Mechanical Completion
Ensure mechanical completion certificates are signed off:
All pipelines are hydrotested.
Valves are tagged and installed in correct direction.
Supports, insulation, and expansion joints are checked.
c. Instrumentation and Control Check
Field transmitters are calibrated.
Control logic in DCS/PLC is verified.
Manual/auto control modes are simulated.
To ensure commissioning decisions are based on reliable data, the instrument validation checklist provides a structured method for verifying sensor accuracy, loop integrity, and signal consistency before relying on live readings.
Poor instrument validation is a major reason for unstable startup and trend misinterpretation.
d. Safety System Validation
Interlocks are tested (for example, low suction trip on compressor).
Emergency shutdown (ESD) system is verified.
Safety relief valves are installed and tagged correctly.
For a full safety review during commissioning and operation:
e. Utilities Readiness
Power supply and earthing system available.
Cooling water, instrument air, and nitrogen purge supply confirmed.
Communication lines and alarms tested.
4. System Preparation & Drying during Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning

Cryogenic systems are highly sensitive to moisture. Even trace water vapor can freeze and block lines during cooldown.
Inadequate drying is one of the most common causes of cold box icing during startup.

a. System Flushing
Flush process lines with clean dry air or nitrogen to remove debris or oil residues.
b. Drying and Purging
Use dry nitrogen purge until dew point < –60°C.
Record dew point readings at multiple locations (cold box, storage lines, exchanger outlet).
Confirm absence of condensate in traps or low points.
c. Leak Testing
Conduct helium or nitrogen pressure tests:
Maintain pressure for 24 hours and monitor for any drop.
Check joints with soap solution or leak detector spray.
Even small air ingress points can introduce moisture and CO₂ into the cold box over time, leading to gradual freezing and pressure drop.
5. Cooldown and Start-Up
Once the system is dry and leak-free, the critical part begins — cooldown and process initiation.
a. Controlled Cooldown
Initiate cooling using gaseous nitrogen in bypass mode.
Monitor temperature drop rate (not more than 10°C per minute to avoid thermal stress).
Gradually introduce cold nitrogen from heat exchangers.
b. Compressor Start-Up
Confirm lube oil and seal gas systems are primed.
Start compressor under manual mode, slowly raise suction pressure.
Verify pressure, temperature, and vibration readings.
c. Cold Box Operation
Maintain proper differential between column and exchanger.
Observe liquid formation rate in separator.
Record data at intervals — column top/bottom temp, pressure, purity.
During cooldown and stabilization, structured trend logging helps detect early instability patterns.
6. Product Purity & Process Stabilization

Once the system reaches cryogenic conditions, attention shifts to product quality and steady-state operation.
a. Purity Verification
Measure nitrogen purity using oxygen analyzer or gas chromatograph.
Target: 99.9% to 99.999% depending on design.
Cross-check analyzer calibration against reference gas.
b. Process Balancing
Adjust column reflux ratio and expansion valve opening.
Maintain cold box pressure balance (avoid column flooding).
Monitor energy consumption vs design value.
c. Safety Checks
Confirm no cold leaks or abnormal vapor clouds.
Verify ESD and alarm functions in cold condition.
Recheck safety interlocks after system stabilizes.
Need pre-commissioning documentation that’s structured and ready for field use?
7. Troubleshooting During Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning

Even a well-planned commissioning can face field challenges.
Here are common troubleshooting issues and recommended approaches.
Many commissioning failures originate from pretreatment instability, refrigeration imbalance, or control tuning errors — not mechanical defects.
| Issue | Likely Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low nitrogen purity | Distillation imbalance | Adjust reflux ratio / column temperature |
| Excessive pressure drop | Ice or blockage | Warm-up and re-dry affected section |
| Vibration in compressor | Unbalanced load or alignment issue | Verify foundation, coupling, and load |
| High liquid carryover | Incorrect reflux or liquid level | Adjust reflux ratio and drain settings |
| Low production rate | Compressor not at design speed | Check suction pressure, motor load |
| Frost formation | Leaks or poor insulation | Inspect and reseal joints |
| Unstable pressure | Faulty control loop | Tune PID parameters |
These quick actions solve surface symptoms, but persistent problems require structured fault isolation.
8. Safety Considerations During Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning

Safety is at the core of cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning. Working with cryogenic temperatures and high-pressure systems demands disciplined adherence to safety procedures.
a. PPE & Safety Practices
Use cryogenic gloves, face shields, and insulated boots.
Keep all personnel trained in cold burn first-aid.
Avoid contact with uninsulated cold surfaces.
b. Oxygen Safety
During cooldown, air ingress may enrich oxygen concentration in vents or enclosures.
Use portable O₂ monitors and ensure proper ventilation.
Oxygen deficiency and enrichment hazards are among the most serious risks during cryogenic commissioning.
c. Pressure Relief & Venting
All vent lines must discharge safely away from personnel.
Relief valves should be verified for correct set pressure and flow direction.
d. Emergency Preparedness
Conduct mock ESD drills before live commissioning.
Define communication chain and control room protocols.
If repeated alarms, leaks, or unsafe conditions appear during commissioning, engineering-level safety review is recommended.
At Graphic Medium Industrial, we emphasize that safe commissioning is not just a checklist activity — it’s a mindset built on training, teamwork, and attention to detail.
9. Documentation & Performance Test for Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning
Performance Guarantee Testing in Cryogenic Nitrogen Plants

After achieving stable operation, the system is validated against design performance.
a. Performance Testing
Record flow, purity, and power consumption over 24 hours.
Compare with design parameters (±5% tolerance typical).
Obtain third-party witness or client sign-off.
If test values fall outside contract limits, see:
b. Documentation Package
Prepare and submit:
Commissioning log sheets
Calibration reports
Safety test certificates
Training and handover documents
Structured documentation prevents disputes and speeds final acceptance.
c. Final Handover
Once performance and documentation are approved, the plant transitions to operations phase.
10. Why Structured Cryogenic Nitrogen Plant Commissioning Matters
A structured cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning plan ensures that every subsystem — mechanical, electrical, instrumentation, and process — performs as a unified system.
Benefits of a structured approach include:
Early detection of mechanical and process defects.
Reduced downtime during the initial production phase.
Better documentation for future maintenance and audits.
Improved nitrogen yield and reduced specific power consumption.
With a digital checklist and documented sequence, engineers can replicate success across multiple projects with consistency and confidence.
Structured commissioning is not just methodology — it requires practical tools engineers can use in the field.
11. Digital Tools & Resources

At Graphic Medium Industrial, our goal is to make technical knowledge digital, structured, and practical for the next generation of engineers.
We offer:
🎁 Free Diagnostic & Safety Checklists
📘 Micro-Books (Focused Technical Topics)
🧰 Toolkits (Full Troubleshooting & Commissioning Systems)
🛠 Consulting Support
Mini-Courses & Training Modules
Focused digital lessons on nitrogen plant commissioning, operation, and safety.
Our digital resources simplify complex processes — helping engineers build clarity, confidence, and readiness for real-world engineering challenges.
Conclusion

Cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning and startup stand as one of the most defining stages in industrial engineering — where safety, precision, and teamwork bring complex systems to life. True success in commissioning goes beyond technical skill; it requires patience, structured execution, and a clear understanding of process behavior under dynamic conditions.
From air compression and purification to cold box separation and final product output, each step in the cryogenic nitrogen plant commissioning process must be systematically verified, recorded, and optimized for long-term reliability and safety.
By following proven commissioning methodologies and applying industry-informed best practices, engineers can achieve smoother startups, minimal downtime, and consistent system performance.
At Graphic Medium Industrial, we convert established engineering principles and commissioning logic into digital knowledge solutions — guides, training modules, and checklists designed to help engineers and technicians work smarter, safer, and faster in today’s evolving industrial landscape.
Engineers who use structured checklists, diagnostic tools, and documented startup sequences consistently achieve faster stabilization and fewer post-startup failures.
Need expert support during commissioning or stabilization?
We provide selective industrial consulting for cryogenic nitrogen plants — focused on startup stabilization, purity recovery, cold box issues, and performance test readiness.
👉 Contact Graphic Medium Industrial Consulting for scope-defined technical support.
FAQ
Q1 — What is the most important step in commissioning a cryogenic nitrogen plant?
A: The systematic verification of all mechanical, instrumentation, and process systems — ensuring safety interlocks, process stability, and design performance before handover.
Q2 — How long does commissioning usually take?
A: Time depends on plant size, site conditions, and system complexity — but planning for a structured sequence with checklists reduces delays and improves accuracy.
Q3 — What tools help engineers during commissioning?
A: Pre-commissioning checklists, cold box temperature maps, instrument validation sheets, and performance test templates significantly improve field accuracy.
